First of all, Wish you all a very very happy new year!
So at the same time a small gift for you is this article.
This article will tell you how to lock files and folders in Windows, Mac and Linux. Sometimes you need to save your private information like results, business documents, private pictures and videos, so the best way is to lock files and folders. If your computer have multi-users and it is used by many users. Then you will definitely need a tool or method to lock files and folders which are private and confidential. As most of the persons in the world mainly use three OS they are Windows, Mac and Linux. so in this tutorial you will learn how to lock files and folders in all three OS. So now don't worry I will tell you how to lock files and folders in simple steps. It's very easy just follow the steps below:
Windows
There are different methods to lock files and folders in windows. I will here tell you three methods. First one will be using programming, Second one using default software's and last is using software's.
- Using Batch File (No Software Needed) :
Step 1. Open the notepad and paste the below code in it.
cls
@ECHO OFF
title Folder Locker
if EXIST "Control Panel.{21EC2020-3AEA-1069-A2DD-08002B30309D}" goto UNLOCK
if NOT EXIST Locker goto MDLOCKER
:CONFIRM
echo Are you sure u want to Lock the folder(Y/N)
set/p "cho=>"
if %cho%==Y goto LOCK
if %cho%==y goto LOCK
if %cho%==n goto END
if %cho%==N goto END
echo Invalid choice.
goto CONFIRM
:LOCK
ren Locker "Control Panel.{21EC2020-3AEA-1069-A2DD-08002B30309D}"
attrib +h +s "Control Panel.{21EC2020-3AEA-1069-A2DD-08002B30309D}"
echo Folder locked
goto End
:UNLOCK
echo Enter password to Unlock folder
set/p "pass=>"
if NOT %pass%==your_Password goto FAIL
attrib -h -s "Control Panel.{21EC2020-3AEA-1069-A2DD-08002B30309D}"
ren "Control Panel.{21EC2020-3AEA-1069-A2DD-08002B30309D}" Locker
echo Folder Unlocked successfully
goto End
:FAIL
echo Invalid password
goto end
:MDLOCKER
md Locker
echo Locker created successfully
goto End
:End
Step 2. Replace "your_password" term in above code with the password you desire. If you not do so then your Default password is "your_passsword" without quotes. Now go to the file menu of the notepad and select Save As option then another window pops out .
in it give name "Locker.bat" and do Save As Type from Text Document to All Files.

Step 3. Now you got the Exe icon like given below. double click that icon.
You will find that a folder with name locker is created there only.
Step 4. put all your important, private files in this newly created folder with name locker.
Step 5. Now after keeping all files, double click on the previous Exe "locker.bat". a command prompt will come and ask to lock folder or not. Press y. your folder is locked now and become invisible too. for making it visible double click on the Exe again and put password.
- Using Default Software :
I had mention the steps please go through it.
Step 1. first create any folder anywhere you want in your system. name it anything. let say xyz.
Step 2.Now put all your important and secret files or the files and folders you need to lock.
Step 3. now right click on that folder do Send To -> Compressed(zipped) Folder.
Step 4. Now a zipped folder is created there only. Double click on it to open. Now a window comes in front of you. In it Go to Files->Set Password.
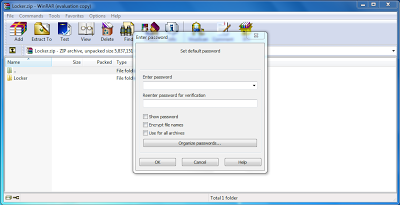

Step 5. Set the desired Password.
Step 6. now delete the original unzipped password.
You are now left with the password protect folder. When someone will try to open it, it will ask password.
- Using Software's :
 Folder Lock 6.4.1
Folder Lock 6.4.1
My Lockbox

Free Hide Folder 3.0
 Folder Lock Free
Folder Lock FreeMicrosoft Private Folder
Linux
In Linux there are two ways one way is lock files and folders using commands and other way is using Software's.
- Using Commands :
Step 1. First create a folder and name it anything. For here let's say u named it abc.
Now give command
[root]# chown -R root:root abc/
Then put this command to change permissions
[root]# chmod -R 700 abc/
To acess folder give this command
sudo nautilus abc
If above commands not work on your Linux then try these
sudo chown -R root:root "folder name" sudo chown 700 "folder name"sudo nautilus "folder name"
- Software's :
If you are using Ubuntu then Open its software center and search for the software named. "ecryptfs". install it by choosing it and then clicking on "install".
Mac
- Software's :
Lock Me Baby
SSH Key Chain
iPhone/ iPad
Download this application. It is the best rated application for locking files and folders.
Download this application. It is the best rated application for locking files and folders.
Folder Lock
If You like this post then Share and Like this on social Site.
Keep Enjoying!






































0 comments: